DINO Series of Self-Supervised Vision Models
#CV #SSL #research/paper
DINO -> self DIstillation with NO labels.
Motivation behind DINO => Self-Supervised Pretraining in NLP was one of the main ingredients for success of Transformers in NLP. Image-Level Supervision reduces the rich concepts present in an image to a single concept, so we don't need any form of image-level supervision.
A few properties that emerge in Self-Supervised ViTs:
- Features explicitly contain the scene layout and object boundaries.
- Features perform well with a basic nearest neighbors classifier without any finetuning.
The second property only emerges when combining momentum encoder with multi-crop augmentation. Usage of small patches is also needed important to improve the quality of the resulting features.
DINO Approach
Architecture of DINO -
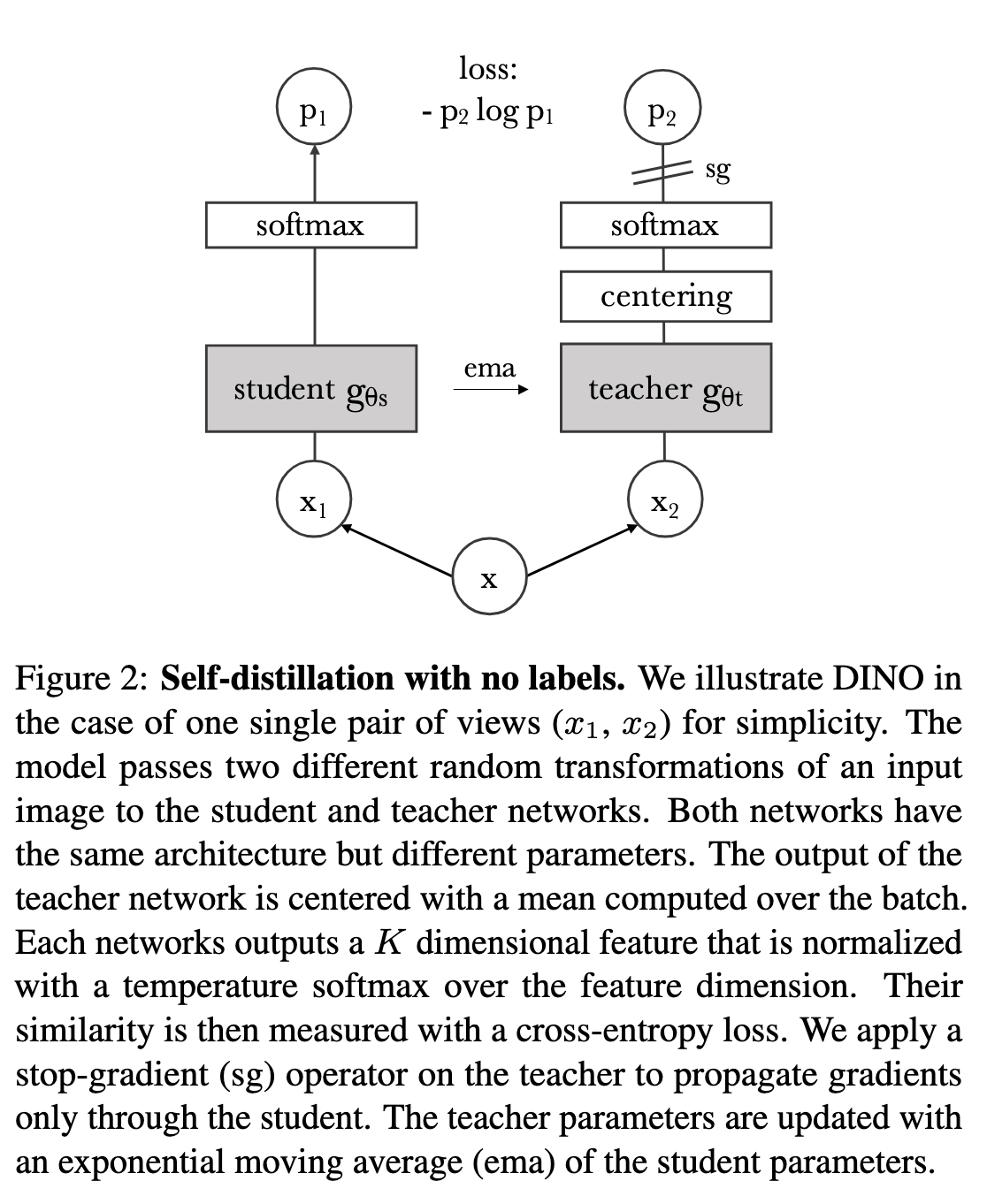
Source - Taken from [@caronEmergingPropertiesSelfSupervised2021]
The approach used in DINO is similar to Knowledge Distillation.
Knowledge Distillation
Student Network
This method of learning a student network is adapted in the case of DINO.
Multi-Crop Strategy
The first step is to generate distorted views and crops of an input image.
From a given image, two global views
Implementation Detail:
2 Global views at 224*224 resolution
Local views at 96*96 resolution
Both the networks have the same architecture
Strategies to update the Teacher Network - Momentum Encoder
Copying the student weight to the Teacher network doesn't work.
However, using an exponential moving average of the student weights works well for the teacher network - Momentum Encoder
where
Lambda goes from 0.996 to 1 during training.
This teacher has better performance than the student at all stages of training. (A Question to Ponder About -> Why is this the case?)
Network Architecture
Composed of a backbone (ViT or ResNet) and a projection head.
For downstream tasks, just use the output of the backbone.
Projection Head - 3 Layer MLP with hidden dim 2048, followed by l2 norm and a weight normalized fully connected layer.
ViT architectures do not use Batch Norm by default. Similarly no BN in the projection heads as well. (Another question to ponder -> Does it work with Batch Norm?)
Avoiding Collapse
Uses Centering and Sharpening of the momentum teacher outputs to avoid model collapse.
Centering prevents one dimension to dominate, but this encourages the model to just give a uniform distribution as it's output. Sharpening has the opposite effect.
Applying both, just balances their effects which is sufficient to avoid collapse in presence of a momentum teacher.
Centering
Adding a bias term
average $$ g_t(x) = g_t(x) + c$$
Sharpening
Use a temperature of less than 0 in softmax, such as 0.04.
A few implementation details
lr = 0.0005 * batchsize/256 .. It is ramped up to this value in the first 10 epochs.
After this, a Cosine schedule with a weight decay of 0.04 to 0.4 is used.
The Temperature is set to 0.1 in the linear warm-up and then 0.04 to 0.07 in the first 30 epochs.
Data augmentations - Color Jittering, Gaussian Blur, Solarization
Ablations in DINO
Patch Size
Smaller Patch Size - better performance but lesser throughput
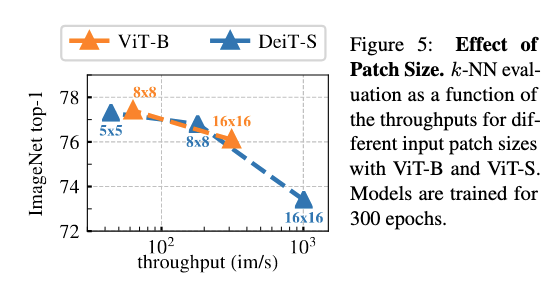
(Image taken from [@caronEmergingPropertiesSelfSupervised2021])
Teacher Network
Using the previous iteration copy of the student as teacher does not converge.
Using the previous epoch copy of the student as teacher converges and gives decent performance.
Momentum performs the best
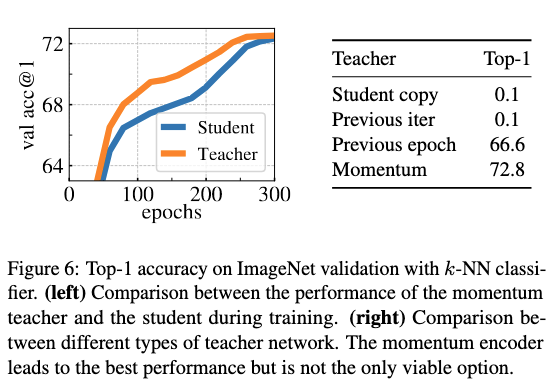
(Image taken from [@caronEmergingPropertiesSelfSupervised2021])
The Teacher outperforming the student at epochs only happens in the case of momentum encoder.
The authors propose to interpret the momentum teacher as some form of Polyak-Rupert Averaging. (This is something to dive into for another day.)
Batch Size
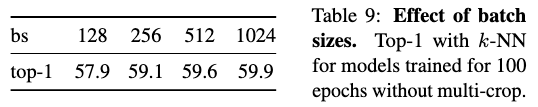
(Image taken from [@caronEmergingPropertiesSelfSupervised2021])
We can train excellent models by using small batch sizes as well.
DINOv2
Image Foundational Models - Models which output features for an image which can then be used for further downstream tasks as it is.
How to make DINO's self supervised learning scale to large scale curated data?
Problem with curated image in the wild data - Rebalancing the concepts present in the images and making sure not just a few dominant concepts are learned.
Data Pipeline
Data Sources - Download Images from a detailed list of sources having both curated sources and uncurated data, then apply PCA hash deduplication, NSFW filtering and blurring identifiable faces.
Deduplication - Uses the pipeline mentioned in [@pizziSelfSupervisedDescriptorImage2022].
Self Supervised Image Retrieval - Build Curated Pre-training dataset by retrieving images similar to those present in the curated dataset.
Uses FAISS library to do retrieval
Core Ideas
Basically the authors took the good ideas of several earlier approaches and brought it together to cook one great dish.
Image-Level Objective
Cross Entropy Loss between the student and teacher network, similar to the loss from DINO. Before generating the probabilities with softmax, they are sent through respective MLP projection heads.
Patch-Level Objective
To enable the model to learn patch-level features, some patches of given to the student are masked, but they are not masked in the teacher.
This technique was introduced in [@zhouIBOTImageBERT2022]
Cross Entropy loss between the student and teacher for the corresponding masked patches.
The heads for DINO and iBOT heads are separate, as the authors empirically found that to work better at scale.
Sinkhorn-Knopp Centering
Introduced in [@caronUnsupervisedLearningVisual2021]
Instead of using the softmax centering from DINO, use an algorithm called the Sinkhorn-Knopp Algorithm for 3 iterations.
The Sinkhorn Algorithm is commonly used to compute optimal transport. However, the crux of it is that given, a positive-valued matrix it tries to make the rows and column sum up to 1. It is an iterative process.
This process used on the teacher's output makes sure that the model tries to use all of the features to represent the entire batch, instead of just relying on output dimension.
KoLeo Regularizer
To further spread out the features, a regularizer is added. It is derived from Kozachenko-Leonenko differential entropy estimator (Added here for clarity, I need to look into this.) It encourages a uniform span of features within a batch.
Given a set of
To calculate it,
- Calculate
- Calculate
Short High res Training
To enable the output features perform well at pixel level downstream tasks, high resolution of the input images is necessary.
However, it is computationally expensive, therefore it trained at a high resolution at the end for a short while.
Implementation Tricks
Sequence Packing
DINO requires to send both the large crops and small crops. When made into patches, they have different lengths, can't be sent together.
We can just concatenate them, but then there will be attention across small crops and large crops. The authors used a block diagonal mask applied to self attention.
Stochastic Depth
An improved version of drop path, that skips the computation of the dropped residuals rather than masking the result.
Fully Sharded Data Parallel (FSDP)
To optimize the model, student, teacher, optimizer first moments, optimizer second moments needs to be in memory. However it leads to 16 GB memory for VIT-g.
To reduce the memory footprint per GPU, FSDP implementation of Pytorch is used.
To reduce the GPU communication costs, some of the data is stored in float16 instead of float32
- Weight Shards for the optimizer - Float32
- the broadcasting weights and reducing gradients of the backbone - Float16
- MLP Heads Weights and Gradients - Float32 to avoid training instabilities
(Note: I plan on writing an in-depth article about FSDP)
Ablation Studies
Training Procedure
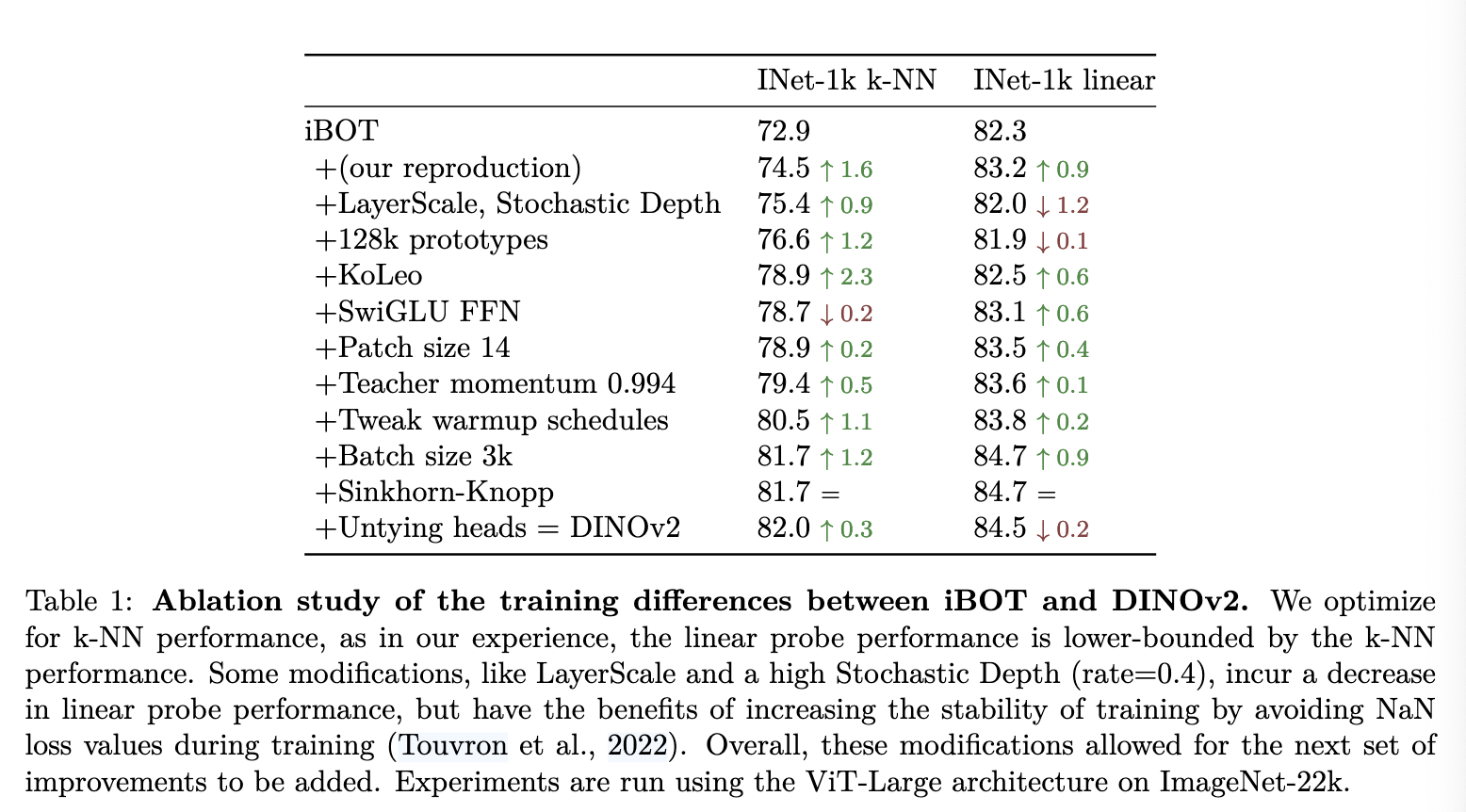
(Image taken from [@oquabDINOv2LearningRobust2024])
From the above table, it is shown that KoLeo Regularizer, Batch Size and changing warmup schedules provide the most gains.
Pre-training Data Source
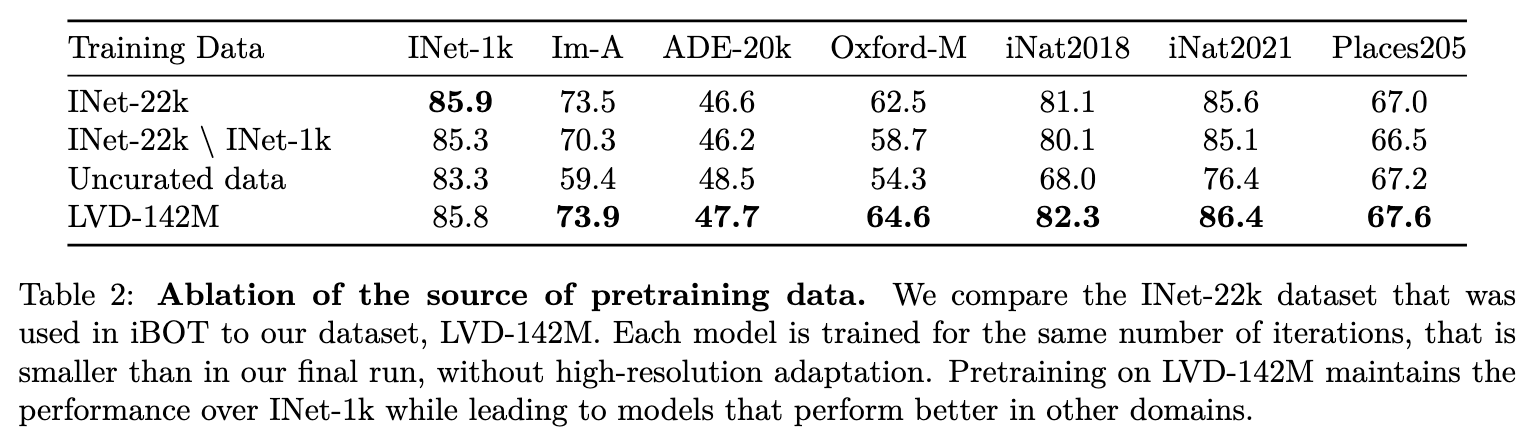
(Image taken from[@oquabDINOv2LearningRobust2024])
Curated Data works better on most of the benchmarks. It is also shown that as the size of the models grow, pre-training on a curated dataset is more important.
Loss Components
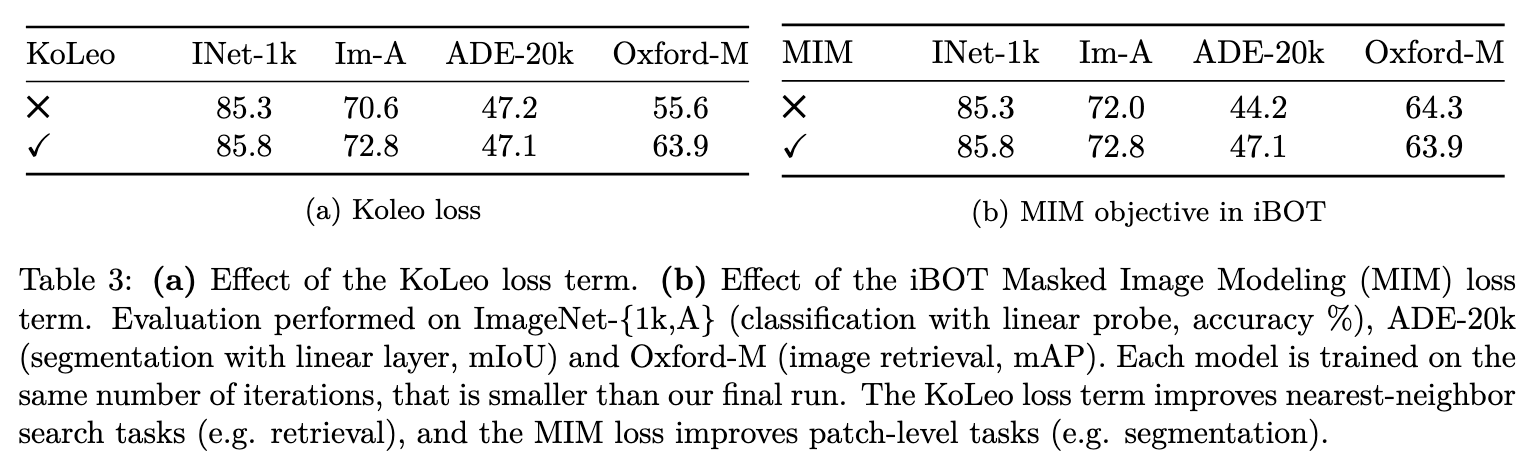
(Image taken from [@oquabDINOv2LearningRobust2024])
KoLeo helps to improve the performance in retrieval and other image level tasks. While Masked Image modelling, helps to improve performance in patch level tasks like segmentation.
Role of High Resolution Training at the end
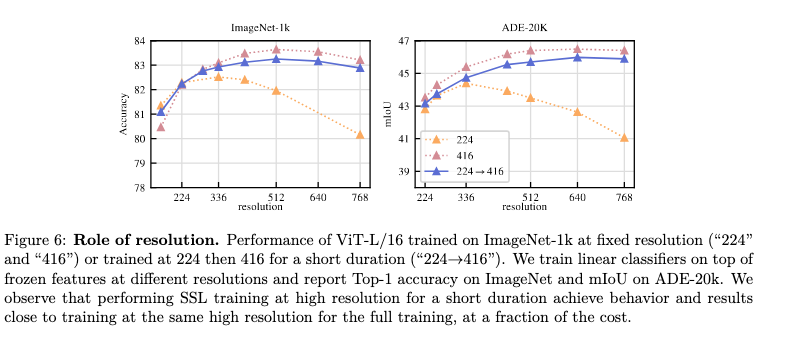
The blue line is the one which represents the training run which trains at a higher resolution in the end.
DINOv3
References
[1]
M. Caron et al., “Emerging Properties in Self-Supervised Vision Transformers,” May 24, 2021, arXiv: arXiv:2104.14294. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2104.14294.
[2]
E. Pizzi, S. D. Roy, S. N. Ravindra, P. Goyal, and M. Douze, “A Self-Supervised Descriptor for Image Copy Detection,” Mar. 25, 2022, arXiv: arXiv:2202.10261. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2202.10261.
[3]
M. Caron, I. Misra, J. Mairal, P. Goyal, P. Bojanowski, and A. Joulin, “Unsupervised Learning of Visual Features by Contrasting Cluster Assignments,” Jan. 08, 2021, arXiv: arXiv:2006.09882. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2006.09882.