QK Norm
Language Models made using Neural Networks have an inherent limitation. It is called the stolen probability effect[1]. It is a byproduct of the dot product distance metric, that enables some words to steal probability from other words due to their relative placement.
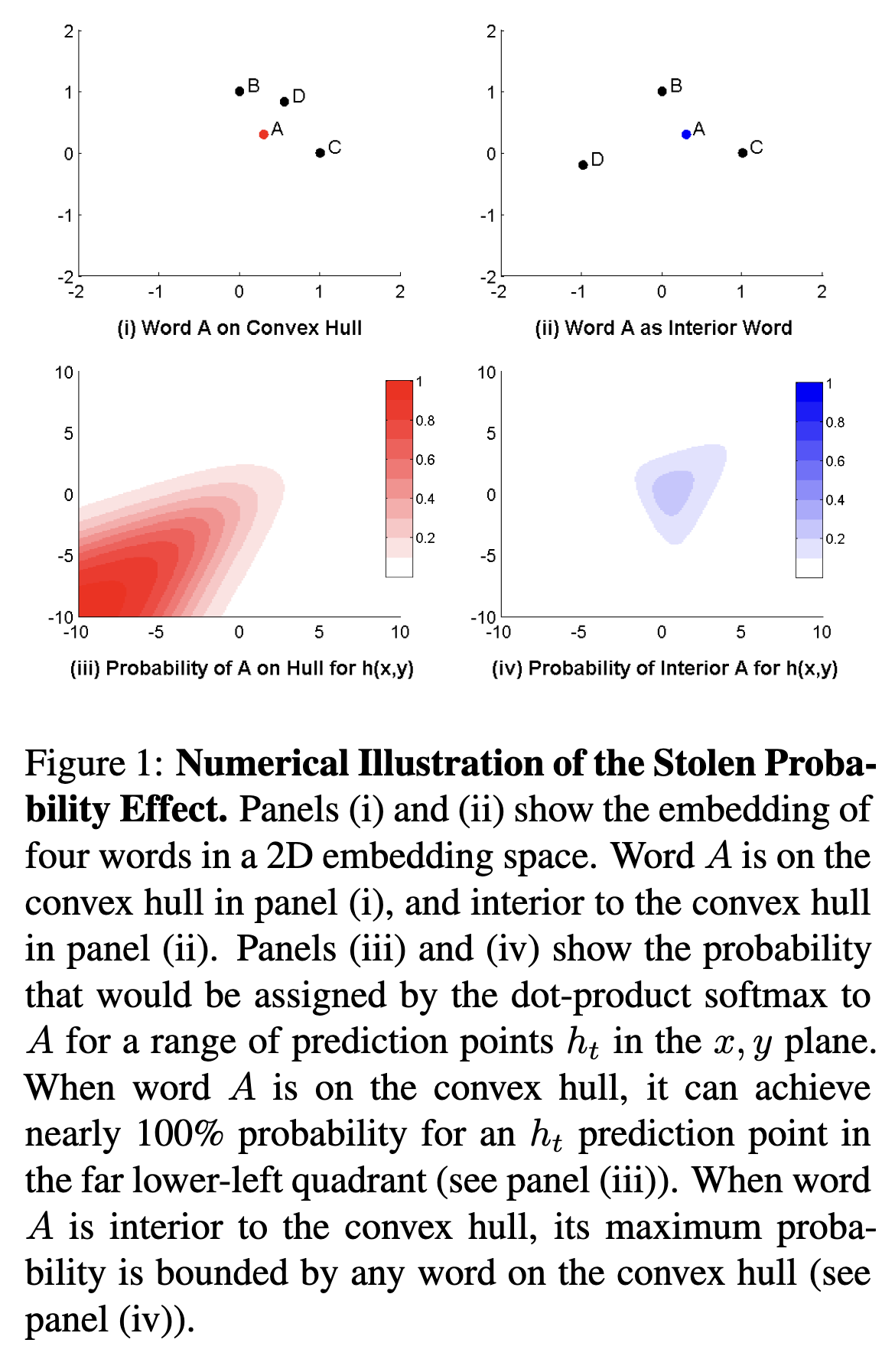
(Image taken from [1])
Basically as seen in the graph on the right, The probability of a word is bound by the probability of it's neighbors.
There is another issue which is related to this as well,
- Softmax - only depends on the differences between values.
- When we do Scaled Dot Product Attention, the dot product is unbounded, the differences maybe insignificantly small on a relative basis. Thus most of the values in the attention map will be close to zero.
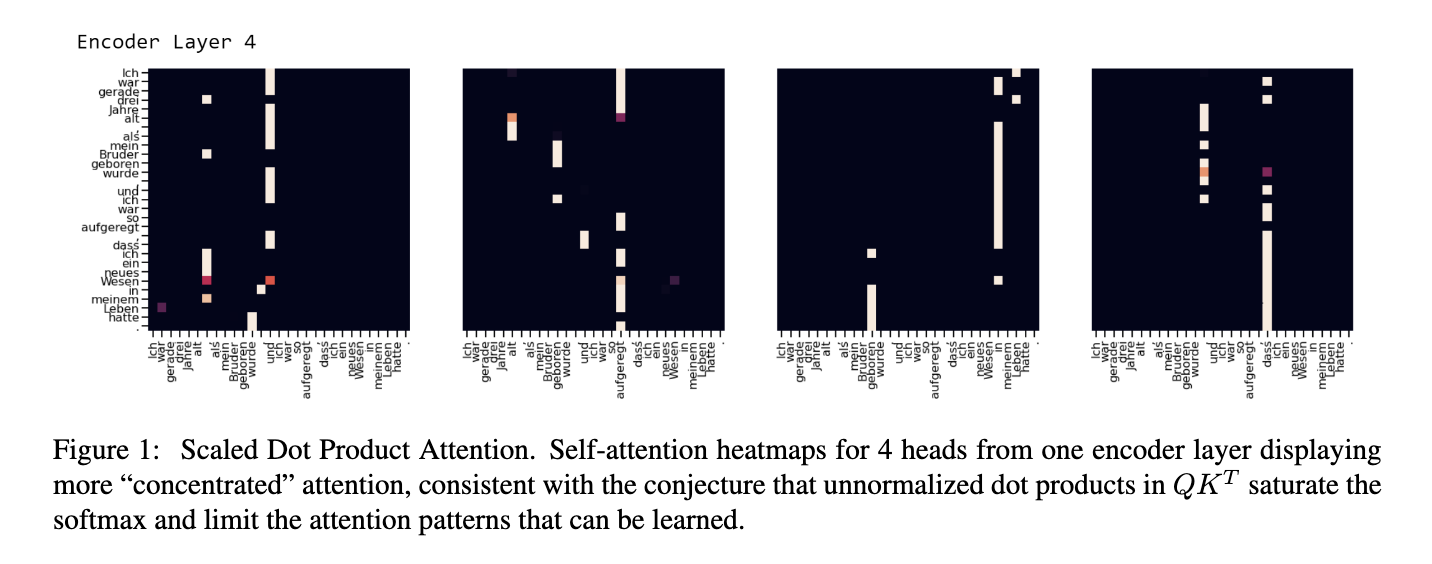
(Image taken from [2])
QK norm(Introduced in [2]) is a solution to this problem.
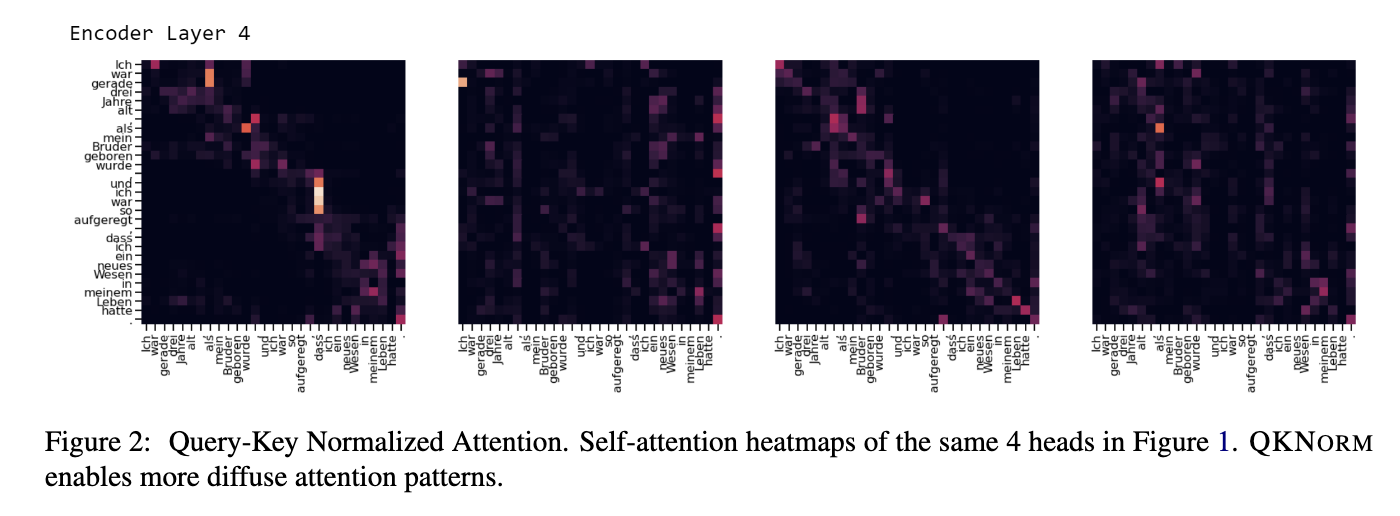
(Image Taken from [2])
The attention operation is changed as follows
where
References
[1]
D. Demeter, G. Kimmel, and D. Downey, “Stolen Probability: A Structural Weakness of Neural Language Models,” in Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, D. Jurafsky, J. Chai, N. Schluter, and J. Tetreault, Eds., Online: Association for Computational Linguistics, Jul. 2020, pp. 2191–2197. doi: 10.18653/v1/2020.acl-main.198.
[2]
A. Henry, P. R. Dachapally, S. Pawar, and Y. Chen, “Query-Key Normalization for Transformers,” Oct. 08, 2020, arXiv: arXiv:2010.04245. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2010.04245.